Diseases & Treatments, Emergency & First Aid, Special Care, Veterinary Science & Advances
Adrenal Gland Tumors in Pets
Topics covered in this article:
- Early Signs of Adrenal Gland Tumors
- Common Types of Adrenal Gland Tumors
- The Importance of Ultrasound, CT, and MRI in Diagnosing Adrenal Gland Tumors
- Treatment Options for Adrenal Gland Tumors
- Post-Treatment Care for Adrenal Gland Tumors
- Conclusion
Adrenal gland tumors in pets are among the most critical endocrine disorders affecting companion animals. These tumors can be either benign or malignant and may lead to significant hormonal imbalances or pressure on nearby organs. Adrenal gland tumors typically present symptoms such as muscle tremors, high blood pressure, weight gain, and excessive drinking. Accurate and timely diagnosis is essential and often requires advanced imaging methods like ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI. In more severe cases, surgical removal or chemotherapy may be necessary. This article explores the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options for adrenal gland tumors, emphasizing the vital role of medical imaging in managing this condition.
Early Signs of Adrenal Gland Tumors
Adrenal gland tumors in pets often begin with subtle symptoms that gradually intensify. Increased water consumption, frequent urination, and restlessness are among the early signs. Other noticeable symptoms include muscle tremors, fatigue, skin thinning or hair loss, and abdominal enlargement—often a result of elevated cortisol levels. Behavioral changes and high blood pressure are also common. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for diagnosing adrenal gland tumors effectively.
Here are key warning signs to help identify adrenal gland tumors in pets:
- Excessive drinking and frequent urination
- Hair loss and thinning skin
- Neurological and behavioral changes
- Unusual weight gain and abdominal swelling
- Hormonal signs specific to adrenal disorders
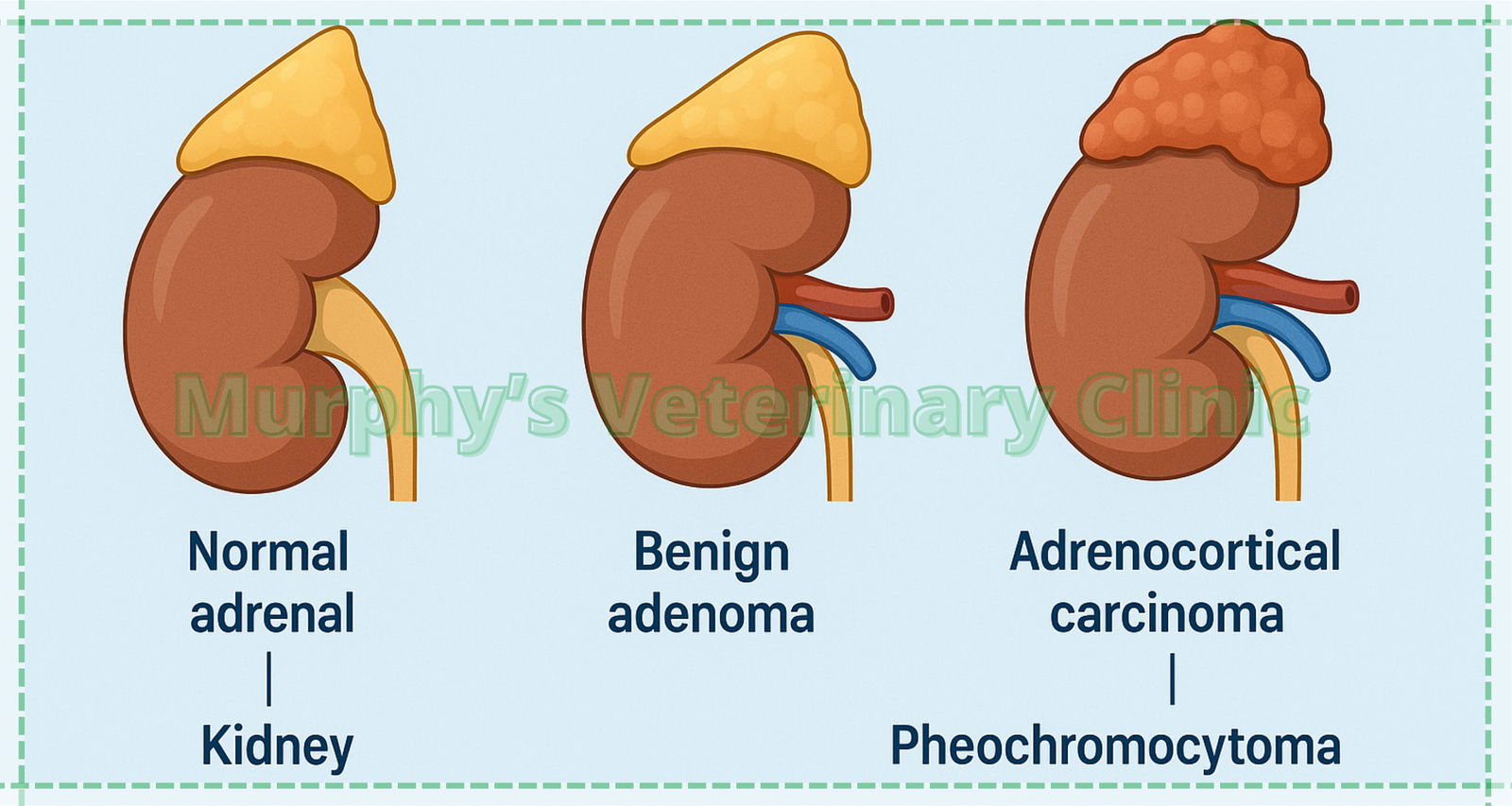
Common Types of Adrenal Gland Tumors
Three primary types of adrenal gland tumors in pets are typically diagnosed: adrenal adenomas, adrenal carcinomas, and non-functional tumors. Adenomas are generally benign and may cause increased cortisol production. Carcinomas are malignant and may secrete cortisol or androgens, significantly impacting the pet’s behavior and health. Non-functional tumors do not produce hormones and are often discovered incidentally. Understanding the tumor type is essential for creating an effective treatment plan for adrenal gland tumors in pets.
Important facts to know about adrenal tumor types in pets:
- Difference between adenomas and carcinomas
- Role of cortisol in hormonal diagnosis
- Asymptomatic tumors detected incidentally
- Aggressive behavior of malignant tumors
- Functional vs. non-functional tumor identification
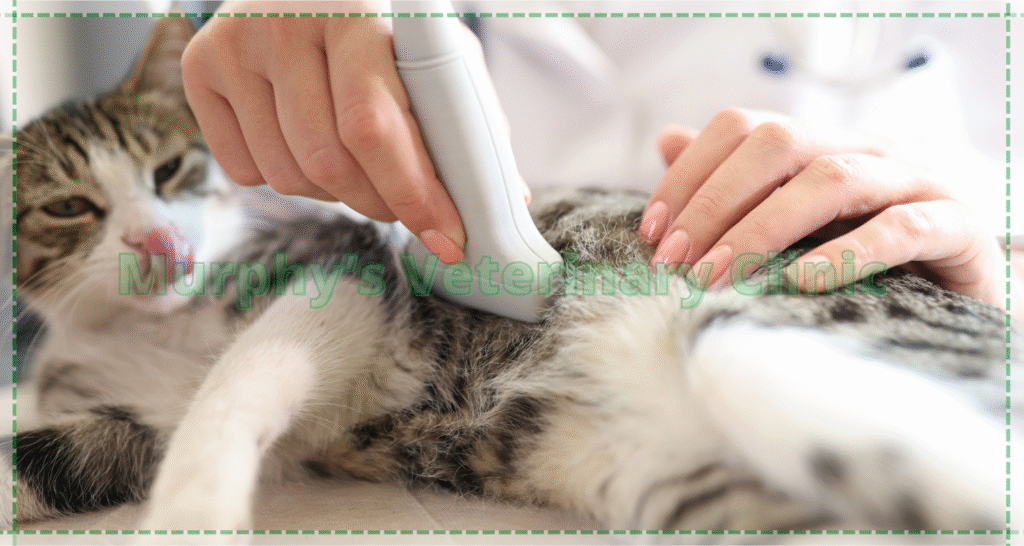
The Importance of Ultrasound, CT, and MRI in Diagnosing Adrenal Gland Tumors
Diagnosing adrenal gland tumors in pets accurately relies heavily on advanced imaging technologies. Ultrasound is often the first step in assessing adrenal gland structure. If abnormalities are found, CT scans provide detailed three-dimensional information about the tumor’s size and location. MRI is the most precise method for identifying the type and spread of the tumor and determining whether surrounding tissues are affected. These tools are essential for forming a complete diagnosis of adrenal gland tumors in pets and deciding the next steps in treatment.
Key imaging insights in adrenal tumor diagnosis:
- Diagnostic power of ultrasound for adrenal evaluation
- CT scans offer detailed tumor mapping
- MRI differentiates between benign and malignant tumors
- Combining imaging with blood tests for accuracy
- Early imaging improves treatment success
Treatment Options for Adrenal Gland Tumors
Treatment for adrenal gland tumors depends on the tumor’s size, type, and hormonal activity. Benign, non-secreting tumors may only require monitoring. Functional or large tumors usually necessitate surgical removal. In cases of malignant tumors, chemotherapy or radiation therapy might be considered. Hormone-regulating drugs can also be prescribed to stabilize the pet’s condition before surgery.
Treatment Options for Adrenal Gland Tumors in Pets
| Treatment Type | Primary Use | Benefits | Limitations |
| Medical Monitoring | Small, benign tumors | Non-invasive, low-cost | Requires regular follow-up |
| Surgery | Large or hormone-secreting tumors | Often curative | Needs anesthesia and recovery |
| Chemotherapy | Malignant tumors | Reduces tumor progression | Potential side effects |
| Hormonal Therapy | Pre-surgery stabilization | Balances endocrine system | Limited to certain tumor types |
Post-Treatment Care for Adrenal Gland Tumors
After treatment, continued care is crucial to manage recovery and prevent recurrence of adrenal gland tumors. Pets that undergo surgery require hormone level monitoring and possibly hormone replacement therapy. Routine blood tests, blood pressure checks, and periodic imaging are essential. Nutrition plans and controlled physical activity also play a role in ensuring long-term recovery.
Post-Treatment Monitoring Plan for Adrenal Tumors
| Care Task | Purpose | Recommended Frequency |
| Follow-up imaging | Check for tumor recurrence | Every 6–12 months |
| Routine bloodwork | Monitor hormone balance | Every 1–3 months |
| Blood pressure check | Prevent dangerous fluctuations | Weekly or monthly |
| Specialized diet | Weight management, hormone support | First 6 months post-treatment |
Conclusion
Adrenal gland tumors in pets are complex but manageable with early detection and tailored treatment. These tumors may cause severe hormonal disruptions and behavioral changes if not treated promptly. Imaging methods such as MRI and CT play a critical role in accurate diagnosis. Treatment options vary from simple observation to surgery and chemotherapy, depending on tumor type. Long-term recovery also hinges on proper aftercare and follow-up. Increasing awareness of adrenal gland tumors in pets among pet owners is key to early diagnosis and successful outcomes.
Murphy’s Veterinary Clinic provides advanced diagnostic services specifically adapted for pets. The clinic’s experienced veterinary team specializes in managing adrenal gland tumors in pets, offering personalized treatment plans that range from surgery to post-operative care. Pet owners can also benefit from continuous follow-up and expert guidance to ensure a full recovery and a healthier life for their companions.


