Diseases & Treatments, Health & General Care, Veterinary Science & Advances
Orthopedic Issues in Pets: Causes and Solutions
Topics covered in this article:
- Trauma-Related Orthopedic Issues in Pets
- Metabolic Diseases and Skeletal Weakness in Pets
- Congenital and Developmental Abnormalities in Bones and Joints
- Hypervitaminosis A and Its Impact on Skeletal Weakness in Pets
- Bone and Joint Cancers in Pets
- Infections and Inflammations in Bones and Joints
- Stress-Related Injuries and Overuse in Pets
- Conclusion
Orthopedic issues in pets are among the most common reasons for veterinary visits. These problems include trauma-related injuries, metabolic diseases, congenital abnormalities, cancers, infections, and stress-related injuries. Ignoring orthopedic issues in pets can lead to chronic pain, mobility restrictions, and even permanent disabilities. Early detection, prevention, and timely treatment are essential to maintaining your pet’s quality of life. In this article, we will explore six major causes of orthopedic issues in pets and provide practical solutions for each. Understanding these causes will help pet owners take preventive actions and seek proper treatment when necessary. Orthopedic issues in pets should never be underestimated as they can escalate into more serious conditions.

Trauma-Related Orthopedic Issues in Pets
Physical trauma is one of the primary causes of orthopedic issues in pets. These injuries often result from accidents, falls, or rough play. Traumatic incidents can cause fractures, joint dislocations, ligament tears, and even spinal injuries. Common signs include sudden lameness, swelling, severe pain, and reluctance to move. Immediate veterinary attention is crucial for accurate diagnosis and prompt treatment. Radiographs and physical examinations help determine the extent of the injury. When addressed early, trauma-related orthopedic issues in pets can often be fully resolved.
- Bone Fractures:
The most frequent injury in falls and accidents, often requiring surgery and splinting. - Joint Dislocations:
Severe joint misalignment that needs urgent repositioning to avoid permanent damage. - Ligament Tears:
Common in energetic dogs, typically treated with surgery and rehabilitation. - Spinal Injuries:
Serious conditions that can lead to paralysis if not treated immediately.
Metabolic Diseases and Skeletal Weakness in Pets
Metabolic disorders such as thyroid dysfunction, vitamin D deficiency, and kidney problems can significantly weaken a pet’s skeletal structure. These diseases reduce bone density, making bones prone to spontaneous fractures. Pets with poor diets or limited sunlight exposure are at higher risk. Blood tests, advanced imaging, and sometimes bone biopsies are required for accurate diagnosis. Addressing these metabolic issues early can prevent severe orthopedic complications in pets.
- Calcium Deficiency:
A leading cause of bone softening and spontaneous fractures due to imbalanced diets. - Thyroid Disorders:
Reduce bone density and increase the likelihood of skeletal deformities. - Kidney Problems:
Disrupt calcium-phosphorus balance, leading to bone weakness. - Lack of Sunlight Exposure:
Results in vitamin D deficiency, impairing bone growth and strength.
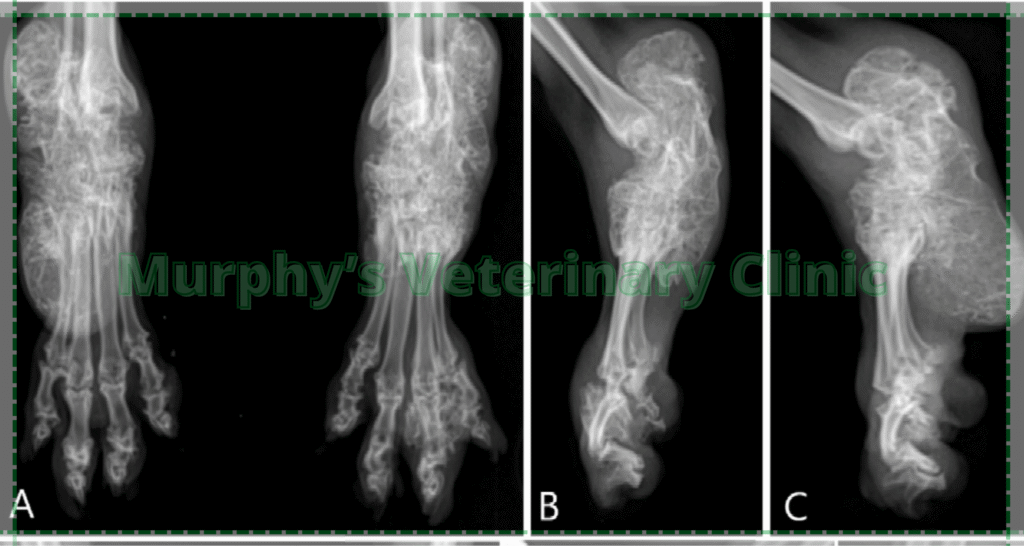
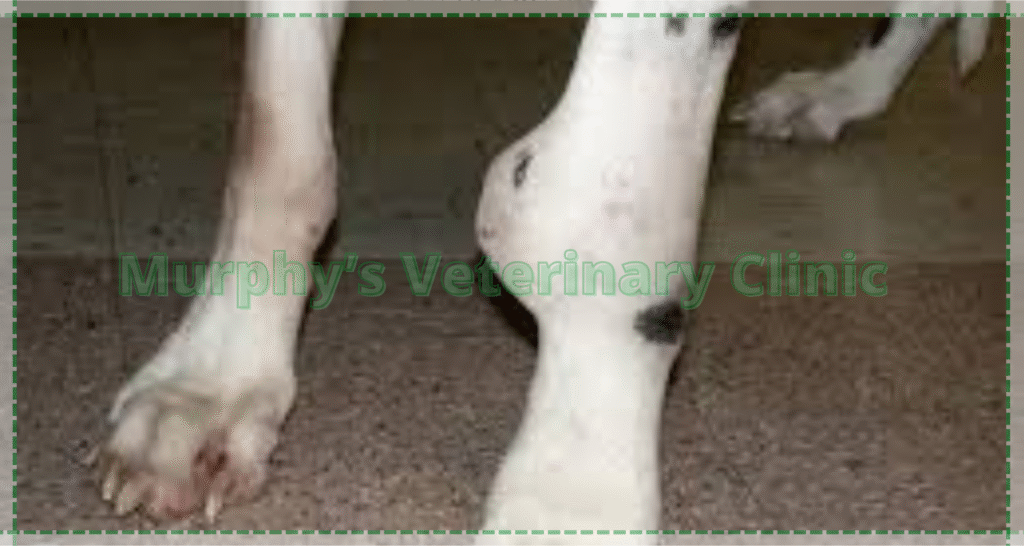
Congenital and Developmental Abnormalities in Bones and Joints
Some pets are born with orthopedic abnormalities due to genetic factors or developmental issues during infancy. Common defects include hip dysplasia, bowed or straight limbs, and disproportionate bone growth. These conditions are prevalent in certain dog and cat breeds and require specialized care. Early diagnosis and corrective treatments such as orthopedic surgery and physical therapy can greatly improve mobility and reduce pain in affected pets.
- Hip Dysplasia:
A prevalent disorder in large dog breeds that can lead to arthritis. - Bone Curvature:
Alters walking patterns and increases the risk of further injuries. - Limb Shortening:
Disrupts body balance due to impaired growth plates. - Joint Formation Defects:
Abnormal joints limit movement and cause chronic discomfort.
Hypervitaminosis A and Its Impact on Skeletal Weakness in Pets
Hypervitaminosis A, caused by excessive vitamin A intake, can result in serious bone and joint issues in pets, especially young cats. It disrupts bone metabolism, leading to abnormal bone growth, stiffness, reduced mobility, and chronic pain. In kittens, it may cause permanent deformities if untreated. A common cause is overfeeding vitamin A–rich foods like liver. Many owners mistakenly consider liver a healthy treat, unaware of its toxicity risk. Preventing this condition requires balanced nutrition and limiting high–vitamin A foods.
Key Risks
- Dietary excess – frequent or large amounts of vitamin A–rich foods.
- Bone growth disruption – causes deformities and stiffness.
- Vulnerability in young cats – higher risk of permanent damage.
- Chronic discomfort – long-term pain from skeletal changes.
High-Risk Foods
Beef or lamb liver, fish liver oil, chicken liver, certain liver-based pet foods, and liver-based homemade treats.
Bone and Joint Cancers in Pets
Bone cancers are among the most severe causes of orthopedic issues in pets. These cancers may be primary, like osteosarcoma, or metastatic, spreading from other body parts. Common symptoms include persistent lameness, localized swelling, intense pain, and pathological fractures. Accurate diagnosis involves radiography, CT scans, and biopsies. Treatment varies based on cancer type and stage, including tumor removal surgery, chemotherapy, and pain management.
| Cancer Type | Initial Symptoms | Diagnostic Method | Recommended Treatment |
| Osteosarcoma | Persistent lameness, bone swelling | Radiography + Biopsy | Surgery + Chemotherapy |
| Chondrosarcoma | Chronic joint pain, stiffness | CT Scan | Tumor Removal Surgery |
| Metastatic Cancers | General weakness, intermittent lameness | Blood Tests + Imaging | Drug Therapy + Supportive Care |
Early diagnosis of bone cancers in pets significantly increases the chances of successful treatment and improves quality of life.
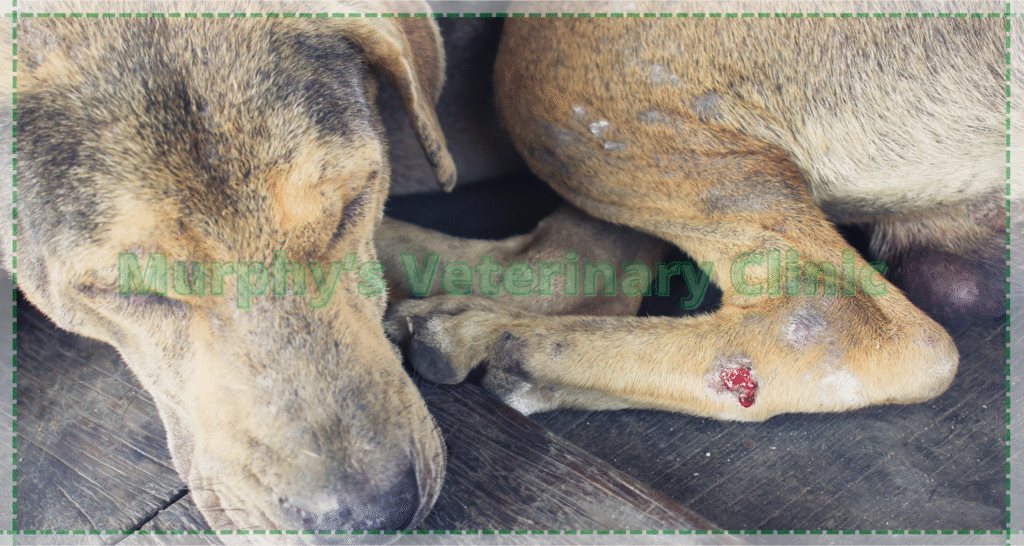
Infections and Inflammations in Bones and Joints
Bacterial or fungal infections can severely damage the bones and joints of pets. These infections often result from open wounds, surgeries, or weakened immune systems. Common signs include swelling, fever, severe pain, and sudden lameness. Infections can spread to bone tissue, causing extensive damage if not treated promptly. Diagnosis involves microbiological cultures and sample testing. Immediate antibiotic therapy and, in severe cases, surgical drainage are essential for treatment.
| Infection Type | Common Cause | Symptoms | Treatment |
| Osteomyelitis | Post-trauma bacterial infection | Fever, pain, lameness | Strong antibiotics + Surgery |
| Septic Arthritis | Microbial invasion of the joint | Joint swelling, intense pain | Injectable antibiotics + Joint lavage |
| Lyme Disease | Tick-borne transmission | Joint pain, fever | Long-term antibiotic therapy |
Delayed treatment of orthopedic infections can result in irreversible tissue damage and permanent disabilities in pets.

Stress-Related Injuries and Overuse in Pets
Stress-related injuries due to excessive or improper activity are a common cause of orthopedic issues in pets. These injuries are frequently observed in highly active or overweight pets. Tendonitis, cruciate ligament injuries, and osteoarthritis are typical examples. Weight management, controlled activity, and the use of orthopedic supplements play a vital role in preventing such injuries.
| Injury Type | Causes | Symptoms | Prevention Method |
| Tendonitis | Overactivity, obesity | Localized pain, lameness | Rest, anti-inflammatory medication |
| Cruciate Ligament Injury | Sudden movements, intense jumping | Sudden lameness, joint swelling | Weight control, activity moderation |
| Joint Wear | Aging, obesity | Stiffness, morning pain | Orthopedic supplements, physiotherapy |
Early detection and proper care for stress-related injuries can prevent progression to more severe orthopedic conditions in pets.
Conclusion
Orthopedic issues in pets can significantly impact their quality of life. These problems stem from various causes, including trauma, metabolic disorders, congenital abnormalities, cancers, infections, and repetitive stress. Timely diagnosis, effective treatment, and preventive care are crucial for managing orthopedic health in pets. Pet owners must be vigilant about early signs of orthopedic issues in pets, as early intervention leads to better outcomes. Maintaining a balanced diet, weight control, regulated physical activity, and regular veterinary visits are essential steps in preventing these problems. Addressing orthopedic issues in pets with proper care ensures a healthier, pain-free life for your beloved companion.
Murphy’s Veterinary Clinic offers advanced imaging technology, a dedicated orthopedic veterinary team, and years of expertise in surgical and rehabilitative care for pets. Our clinic provides personalized treatment plans, including orthopedic surgeries, specialized physiotherapy, and nutritional counseling to support your pet’s orthopedic health. If your pet is experiencing lameness or skeletal discomfort, Murphy’s is your best choice for professional and comprehensive care.


