Diseases & Treatments, Emergency & First Aid, Health & General Care
Trauma-Related Pet Orthopedic Issues
Topics covered in this article:
- Bone Fractures in Pets with Orthopedic Trauma
- Joint Dislocations After Trauma in Pets
- Ligament Tears as Orthopedic Trauma in Pets
- Spinal Injuries from Trauma in Pets
- Joint Inflammation Post-Trauma in Pets
- Conclusion
Trauma-Related Pet Orthopedic Issues are among the most frequent conditions treated in veterinary clinics. Accidents, falls, and rough play are primary causes of these injuries, which include fractures, joint dislocations, ligament tears, spinal injuries, and joint inflammations. Recognizing early symptoms—like sudden limping, swelling, and reluctance to move—can significantly improve recovery outcomes. Prompt veterinary intervention is essential to address orthopedic injuries caused by trauma in pets. Diagnostic imaging and thorough examinations help determine the severity of injuries and guide effective treatment strategies.
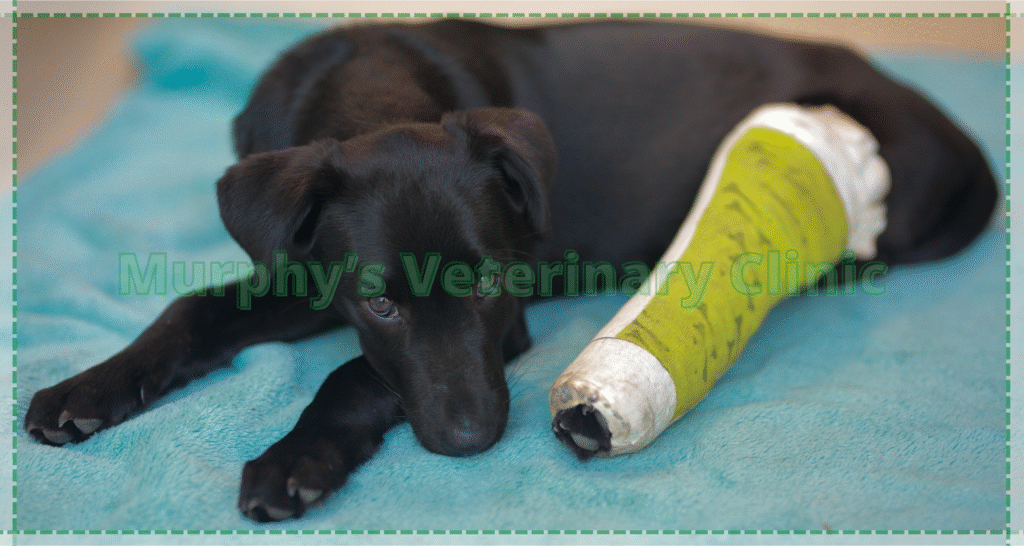
Bone Fractures in Pets with Orthopedic Trauma
Bone fractures are one of the most common orthopedic injuries resulting from pet trauma. These fractures can vary from minor cracks to severe compound breaks that require surgical repair. Addressing pet bone fractures promptly ensures faster healing and minimizes long-term complications. Treatment typically involves surgical stabilization, followed by rest and controlled rehabilitation to restore full mobility. Treatment depends on the type of fracture and can vary from non-surgical techniques to surgical immobilization.
Types of Bone Fractures in Pet Orthopedic Trauma
| Fracture Type | Description |
| Simple Fracture | A clean break without bone displacement |
| Compound Fracture | Bone pierces through the skin |
| Comminuted Fracture | Bone shatters into multiple pieces |
| Intra-Articular | Fracture extends into the joint space |
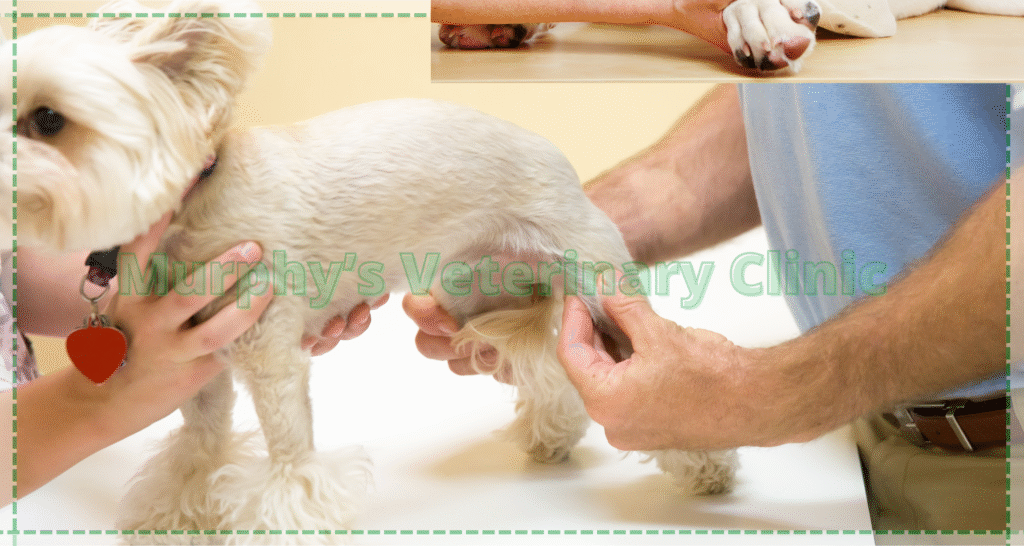
Joint Dislocations After Trauma in Pets
Joint dislocations are serious injuries that can cause severe discomfort and mobility issues for pets. These dislocations, often due to falls or accidents, require immediate veterinary attention. Repositioning the joint and stabilizing it are critical steps in preventing permanent damage. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair damaged ligaments and tissues.
- Common Causes of Dislocations
Falls from height, vehicular accidents, and rough play. - Symptoms of Joint Misalignment
Noticeable joint deformity, swelling, and inability to bear weight. - Diagnostic Procedures
Physical examination and X-rays are essential for accurate assessment. - Rehabilitation and Aftercare
Immobilization followed by structured physiotherapy sessions.
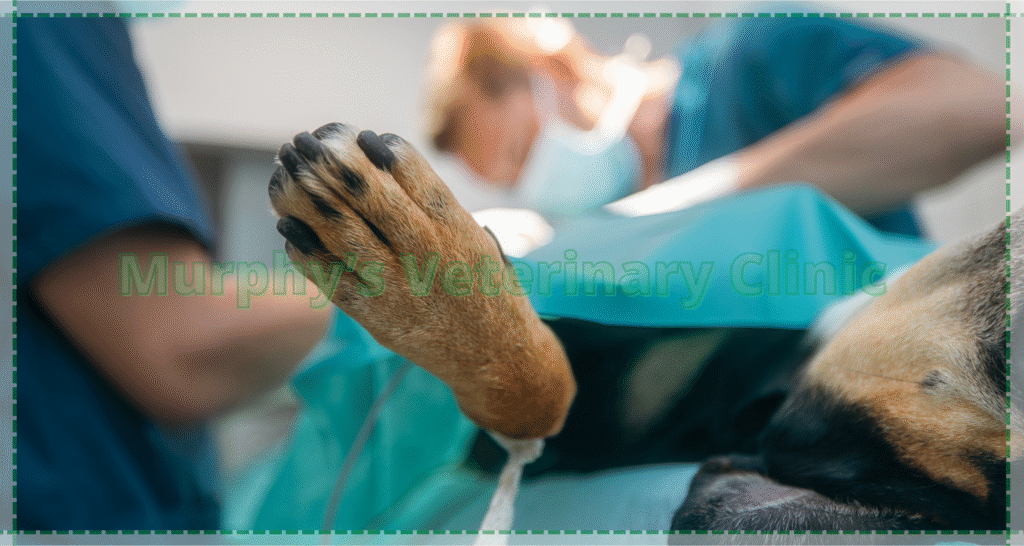

Ligament Tears as Orthopedic Trauma in Pets
Ligament tears, particularly in active dogs, are common orthopedic injuries resulting from trauma. One of the most frequent is the cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) tear. Such injuries lead to lameness and require surgical repair for stabilization. A carefully designed rehabilitation program is crucial for restoring joint functionality post-surgery.
- Diagnosing Ligament Injuries
Orthopedic examinations combined with imaging tests. - Surgical Techniques for Repair
Intracapsular technique and extracapsular technique like TPLO, TTA. - Post-Surgical Rehabilitation
Gradual increase in physical activity under supervision. - Preventative Care Post-Recovery
Weight management and controlled exercise to avoid reinjury.
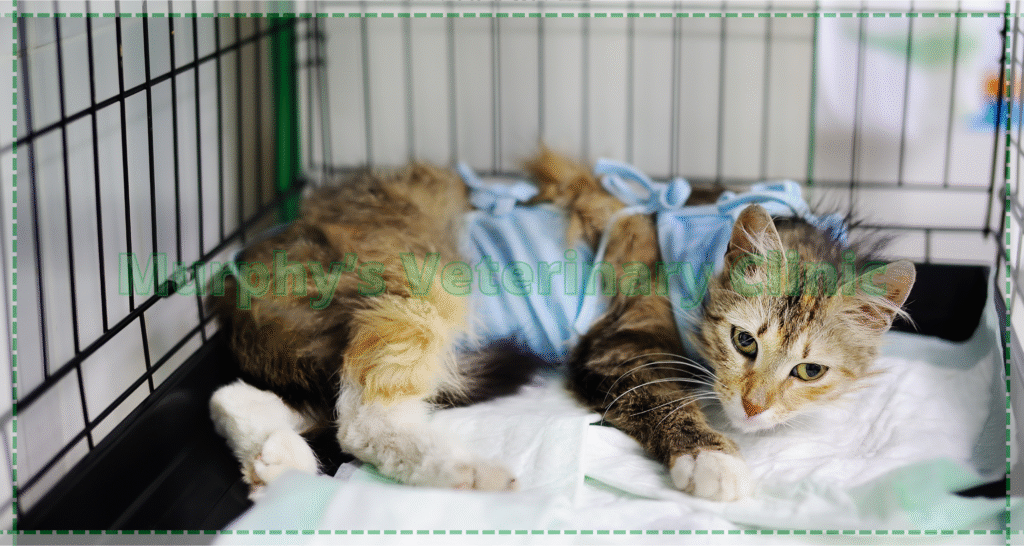

Spinal Injuries from Trauma in Pets
Spinal injuries are among the most severe complications following trauma in pets, with the potential to cause paralysis. Immediate diagnosis and intervention are critical to prevent permanent neurological damage. Surgical decompression of the spinal cord is often required, followed by intensive rehabilitation therapy to aid recovery.
Severity Levels of Spinal Injuries in Pets
| Injury Grade | Symptoms | Treatment Approach |
| Mild | Temporary weakness and numbness | Medication and physical therapy |
| Moderate | Partial or full hindlimb paralysis | Surgical decompression and rehabilitation |
| Severe | Complete paralysis and incontinence | Emergency surgery and long-term care |

Joint Inflammation Post-Trauma in Pets
Joint inflammation can develop as a secondary complication after fractures, dislocations, or ligament injuries in pets. Inflammatory responses lead to swelling, stiffness, and discomfort, affecting the pet’s mobility. Effective management includes anti-inflammatory medications, physiotherapy, and in severe cases, surgical correction of joint structures.
- Causes of Post-Trauma Inflammation
Repeated strain on injured joints and delayed healing. - Recognizing Inflammatory Symptoms
Persistent swelling, reduced range of motion, and pain. - Non-Surgical Treatments
Anti-inflammatory medications and joint health supplements. - Surgical Intervention for Chronic Cases
Reconstructive procedures to restore joint functionality.
Conclusion
Trauma-Related Pet Orthopedic Issues demand timely recognition and immediate care. Early intervention not only improves treatment success but also minimizes the risk of long-term disability. Fractures, dislocations, ligament tears, spinal injuries, and joint inflammations all fall under trauma-related orthopedic conditions that require specialized veterinary attention. Pet owners should remain vigilant and collaborate closely with their veterinarians to ensure comprehensive care and rehabilitation. Effective management of orthopedic trauma in pets leads to full recovery and enhances their quality of life.
Murphy’s Veterinary Clinic offers advanced diagnostic, surgical, and rehabilitation services specifically designed for Trauma-Related Pet Orthopedic Issues. The clinic’s experienced team ensures personalized treatment plans that address each pet’s unique needs. With state-of-the-art equipment and expert follow-up care, Murphy’s Veterinary Clinic is the trusted choice for pet owners seeking comprehensive solutions for trauma-related orthopedic problems.



Pingback: Orthopedic Issues in Pets: Causes and Solutions - MURPHYS Veterinary Clinic