Diseases & Treatments, Health & General Care, Veterinary Science & Advances
Orthopedic Surgeries in Pets
Topics covered in this article:
- Fixing Broken Bones: How We Treat Fractures in Pets
- What to Expect If Your Dog Needs Cruciate Ligament Surgery
- Fracture Repair in Dogs and Cats: Techniques and Recovery Tips
- Hip Dysplasia and Surgical Options: What Pet Owners Need to Know
- Rehabilitation After Orthopedic Surgery: Helping Pets Regain Mobility
- Conclusion
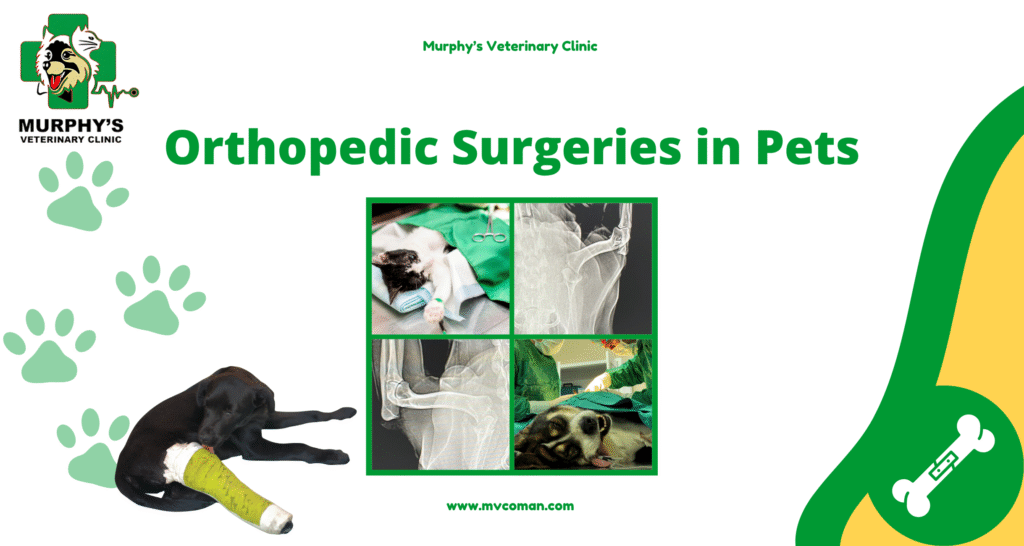
Orthopedic Surgeries in Pets represent one of the most advanced fields of veterinary medicine, focusing on diagnosing, correcting, and restoring the musculoskeletal system — including bones, joints, tendons, and ligaments. These procedures are not limited to fractures; they also address congenital deformities, degenerative conditions, and trauma-related injuries. The main goal of Orthopedic Surgeries in Pets is to restore natural mobility, reduce pain, and improve quality of life. Through advanced surgical techniques, veterinarians can reconstruct damaged structures and enhance stability. In recent years, the use of orthopedic implants such as plates, pins, and screws has significantly increased surgical success rates. Moreover, postoperative physiotherapy and controlled rehabilitation play vital roles in recovery. With early intervention and professional care, Orthopedic Surgeries in Pets can help animals regain their ability to walk, run, and live pain-free lives.
Fixing Broken Bones: How We Treat Fractures in Pets
Bone fractures in pets are commonly caused by accidents, falls, or severe trauma. In Orthopedic Surgeries in Pets, the veterinarian first determines the fracture type using radiography or CT scans. Treatment options vary — from external splinting and casting to internal fixation using orthopedic pins, plates, or screws. Complex fractures often require Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) to realign and stabilize the bone. Proper anesthesia management and aseptic techniques are essential for successful healing. After surgery, pain management through NSAIDs and restricted activity are crucial. Follow-up X-rays help monitor bone union and detect complications like delayed healing or infection. With proper care, Orthopedic Surgeries in Pets can ensure full functional recovery and long-term bone strength.
- Types of fractures in companion animals
- Fracture stabilization methods in veterinary orthopedics
- Advanced surgical tools and fixation techniques
- Postoperative care and pain management
What to Expect If Your Dog Needs Cruciate Ligament Surgery
Among Orthopedic Surgeries in Pets, cruciate ligament surgery is one of the most frequent procedures in dogs. The cranial cruciate ligament (CCL), similar to the ACL in humans, stabilizes the knee joint. When torn or inflamed, it causes lameness, joint swelling, and discomfort. Diagnosis is based on orthopedic examination, the tibial compression test, and diagnostic imaging such as X-rays or arthroscopy. Surgical techniques such as TPLO (Tibial Plateau Leveling Osteotomy), TTA (Tibial Tuberosity Advancement), or Extra-Capsular Repair are performed depending on the dog’s size and activity level. These surgeries restore joint stability and prevent degenerative joint disease (DJD). Post-surgical rehabilitation, including controlled exercise and physiotherapy, is essential for recovery. With timely intervention, Orthopedic Surgeries in Pets like CCL repair can restore pain-free movement and reduce long-term complications.
- Common symptoms of cruciate ligament injury
- Clinical diagnosis and imaging techniques
- Surgical options for cruciate ligament repair
- Rehabilitation and physiotherapy after surgery
Fracture Repair in Dogs and Cats: Techniques and Recovery Tips
Orthopedic Surgeries in Pets involving fracture repair are complex and depend on the animal’s age, size, and fracture pattern. Stabilization techniques may include intramedullary pinning, bone plating, or external skeletal fixation (ESF). Younger animals tend to heal faster due to active bone remodeling, but they require careful postoperative supervision. During surgery, maintaining proper alignment and minimizing soft tissue damage are essential to promote osteogenesis. Postoperative radiographs are used to evaluate bone callus formation and monitor healing progression. Controlled rest, anti-inflammatory medications, and gradual physiotherapy enhance recovery outcomes. Additionally, dietary calcium and vitamin D supplementation can support bone regeneration. With advanced imaging and precise surgical planning, Orthopedic Surgeries in Pets provide excellent long-term functional results.
- Factors influencing fracture repair success
- Preoperative preparation and surgical planning
- Modern fixation systems in veterinary orthopedics
- Postoperative rehabilitation and exercise routines
Hip Dysplasia and Surgical Options: What Pet Owners Need to Know
Hip dysplasia is a common orthopedic disorder, especially in large-breed dogs, caused by abnormal development of the hip joint. Orthopedic Surgeries in Pets for this condition include Femoral Head Ostectomy (FHO), Total Hip Replacement (THR), and Triple Pelvic Osteotomy (TPO). Early detection through radiographs or PennHIP evaluation can prevent progression to osteoarthritis. The choice of surgery depends on the pet’s age, weight, and severity of joint degeneration. Pain control with analgesics, physical therapy, and weight management are crucial after surgery. These advanced procedures reduce pain, improve mobility, and restore normal gait patterns. With the right surgical technique and proper postoperative care, Orthopedic Surgeries in Pets can significantly extend the lifespan and comfort of affected animals.
Common Hip Dysplasia Surgeries and Their Benefits
| Surgical Technique | Objective | Healing Time | Success Rate | Postoperative Recommendation |
| FHO (Femoral Head Ostectomy) | Eliminate joint pain | 6–8 weeks | High | Restricted movement and rest |
| Total Hip Replacement (THR) | Restore full joint function | 8–12 weeks | Very High | Daily physiotherapy sessions |
| Hip Joint Resurfacing | Reduce joint friction | 4–6 weeks | Moderate | Maintain ideal body weight |
| Triple Pelvic Osteotomy (TPO) | Realign joint in young dogs | 8 weeks | High | Close postoperative monitoring |
Rehabilitation After Orthopedic Surgery: Helping Pets Regain Mobility
Rehabilitation is the final and most essential stage of Orthopedic Surgeries in Pets. It helps restore range of motion, strengthen muscles, and prevent stiffness or contractures. Rehabilitation programs include manual physiotherapy, hydrotherapy, laser therapy, and weight management. Veterinarians design individualized rehabilitation plans based on the type of surgery and the animal’s condition. Controlled exercises such as passive limb movement, balance training, and underwater treadmill sessions improve circulation and prevent muscle atrophy. Regular follow-ups ensure proper joint function and detect early complications. Nutrition rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants supports faster recovery. When combined with surgical precision, Orthopedic Surgeries in Pets followed by proper rehabilitation lead to optimal long-term outcomes.
Common Rehabilitation Techniques After Orthopedic Surgery
| Rehabilitation Method | Main Purpose | Frequency | Duration per Session | Key Benefit |
| Manual Physiotherapy | Improve joint flexibility | Daily | 20 minutes | Prevent stiffness and adhesions |
| Hydrotherapy | Reduce joint stress | 3 times weekly | 30 minutes | Strengthen muscles safely |
| Laser Therapy | Minimize inflammation | Twice weekly | 15 minutes | Accelerate tissue repair |
| Weight Control | Prevent excess joint load | Ongoing | — | Maintain optimal mobility |
Conclusion
Orthopedic Surgeries in Pets are vital procedures that restore mobility, comfort, and overall quality of life for animals suffering from musculoskeletal disorders. Thanks to technological advancements such as digital radiography, arthroscopy, and improved anesthesia, surgical success rates have risen significantly. From fracture repairs to joint replacements, every step requires careful planning, precision, and diligent postoperative care. Pet owners play a crucial role by ensuring proper nutrition, rest, and physiotherapy compliance. Early diagnosis and timely surgery can prevent irreversible joint damage. Ultimately, Orthopedic Surgeries in Pets not only heal injuries but also help prevent chronic pain and degenerative diseases. With expert guidance, pets can enjoy a healthy, active, and pain-free life.
At Murphy’s Veterinary Clinic, a team of experienced surgeons specializes in Orthopedic Surgeries in Pets, offering advanced diagnostic, surgical, and rehabilitation services. The clinic is equipped with modern imaging systems, sterile surgical suites, and dedicated recovery units. Every case is evaluated individually to determine the most suitable treatment plan — whether it’s fracture repair, ligament reconstruction, or joint replacement. The clinic’s comprehensive physiotherapy and follow-up programs ensure complete and safe recovery. Murphy’s Veterinary Clinic is committed to restoring mobility, reducing pain, and enhancing the overall well-being of every pet through state-of-the-art orthopedic care.