Diseases & Treatments, Health & General Care, Veterinary Science & Advances
Bone and Joint Infections
Topics covered in this article:
- Common Causes
- Signs and Symptoms
- Diagnostic Methods for Bone and Joint Infections
- Treatment
- Prevention
- Conclusion
Bone and Joint Infections are serious musculoskeletal conditions that can significantly impact mobility and overall health. These disorders may arise from microbial agents such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi, or from chronic inflammatory responses. Bone and Joint Infections not only cause pain and reduced range of motion but, if left untreated, can lead to structural destruction of bones or joints. Early diagnosis is crucial, as timely treatment can prevent disease progression. In many cases, Bone and Joint Infections start with non-specific symptoms, which can delay detection. Therefore, patient and clinician awareness of the signs and risk factors is essential. Managing these conditions requires a multidisciplinary approach, including pharmacological therapy, surgery, and rehabilitation. This article explores the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and prevention strategies related to Bone and Joint Infections.

Common Causes
Bone and Joint Infections may result from various sources. One primary cause is the direct entry of bacteria or other pathogens into bone or joint tissue, often following open injuries or orthopedic surgeries. Hematogenous spread, where infection travels through the bloodstream from another site, is another significant mechanism. In some cases, abnormal immune responses against the body’s own tissues trigger inflammation. Additionally, trauma and fractures can create favorable conditions for pathogens to thrive. Understanding these causes is essential for effective prevention and treatment of this.
- Direct bacterial infections
- Hematogenous spread from other sites
- Trauma and fractures
Signs and Symptoms
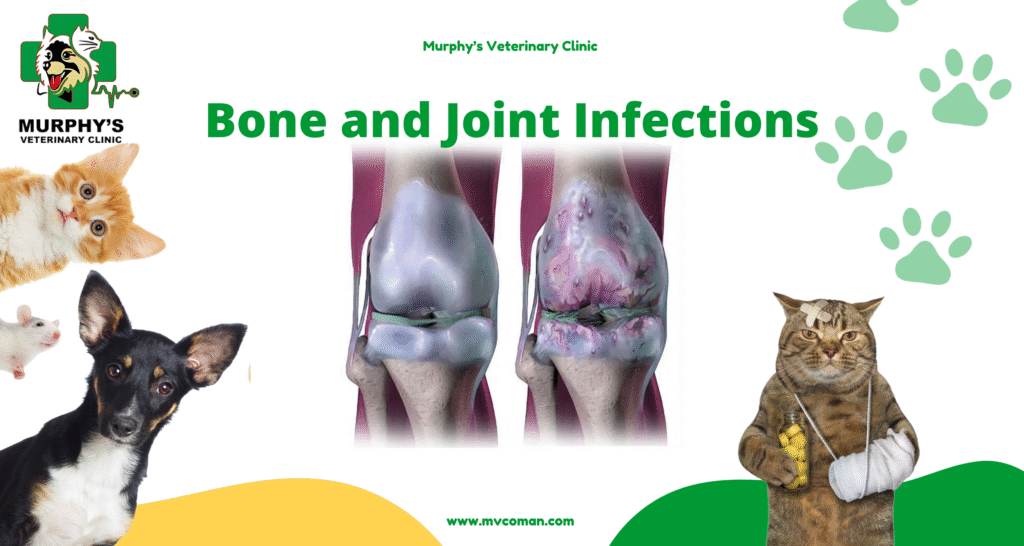
The diagnosis of Bone and Joint Infections often begins with the recognition of key clinical features. Severe, persistent pain that worsens with movement or pressure is one of the most common signs. Localized swelling and redness occur due to the body’s inflammatory response. Reduced mobility may result from pain and structural damage to the joint or bone. In some cases, fever and chills indicate the presence of a systemic infectious process. Careful assessment of these symptoms by a healthcare professional enables early diagnosis and prompt initiation of treatment for this.
- Severe and persistent pain
- Localized swelling and redness
- Restricted joint movement
- Fever and chills
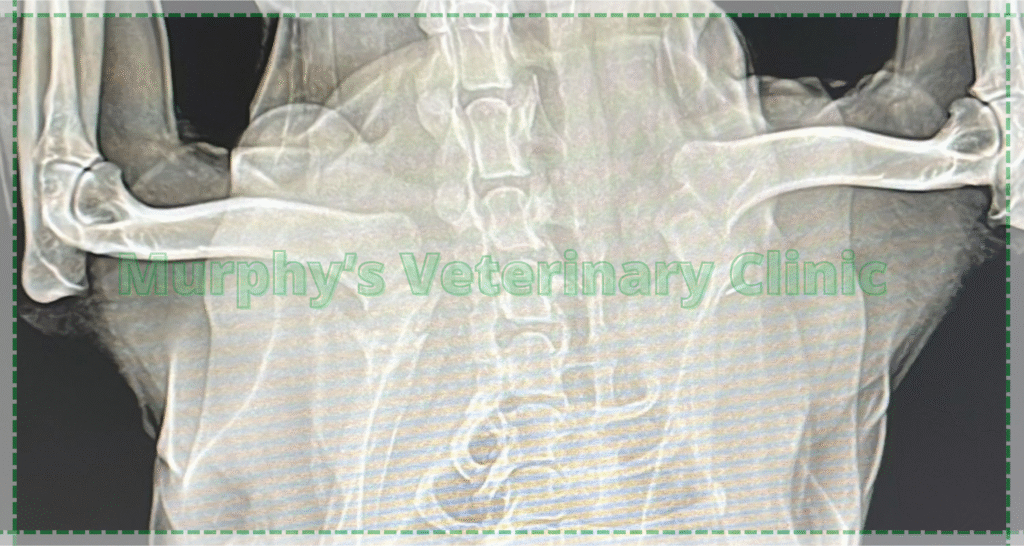
Diagnostic Methods for Bone and Joint Infections
Accurate diagnosis of bone and joint infections requires both imaging and laboratory evaluations. Radiographic imaging can reveal structural changes in the affected bone, while MRI and CT scans provide detailed visualization of soft tissue and bone involvement, helping to pinpoint the site of infection or inflammation. Blood tests, such as CBC, serve as important indicators of inflammatory activity. In certain cases, a tissue biopsy may be performed to identify the causative microorganism and guide targeted therapy.
- Radiographic imaging
- MRI and CT scans
- Blood tests
- Tissue biopsy

Treatment
Treatment for Bone and Joint Infections typically involves a combination of pharmacological and surgical interventions. Antibiotics, selected based on the identified pathogen, may be prescribed for extended durations. When pus accumulation or necrotic tissue is present, surgical debridement becomes necessary. Anti-inflammatory drugs help reduce pain and swelling, while physiotherapy and rehabilitation restore mobility and function after infection control.
| Treatment Method | Description |
| Antibiotic therapy | Use of targeted antimicrobial agents |
| Surgical debridement | Removal of infected or necrotic tissue |
| Anti-inflammatory drugs | Reduction of pain and swelling |
| Physiotherapy | Restoration of mobility and strength |

Prevention
Prevention plays a vital role in reducing the incidence of Bone and Joint Infections. Maintaining strict surgical hygiene, providing proper wound care, and promptly treating systemic infections can prevent disease spread. Additionally, vaccination and controlling chronic illnesses such as diabetes can lower the risk of developing Bone and Joint Infections.
| Preventive Measure | Description |
| Surgical hygiene | Preventing contamination during procedures |
| Wound care | Keeping injuries clean and dry |
| Vaccination | Protecting against infectious diseases affecting bones and joints |
| Chronic disease control | Reducing infection risk through proper management |
Conclusion
Bone and Joint Infections are among the most critical orthopedic conditions, capable of severely affecting patients’ quality of life. Early detection and appropriate management can prevent progression and irreversible damage. The causes, clinical manifestations, diagnostic tools, and treatment strategies for these infections are diverse, requiring a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach. Patient education regarding early signs and preventive measures plays a crucial role in reducing the incidence and severity of this. Post-surgical care and personal hygiene are also essential in minimizing risks. Advances in medical research promise more effective treatments in the future. By fostering collaboration between healthcare providers, patients, and specialized clinics, the burden can be significantly reduced.
Murphy’s Veterinary Clinic, equipped with advanced diagnostic tools and a highly trained medical team, provides comprehensive care for Bone and Joint Infections in animals. The clinic utilizes state-of-the-art imaging, laboratory, and surgical techniques to create personalized treatment plans. Preventive programs and expert consultations are also offered to reduce the risk of these conditions in pets, ensuring their mobility, comfort, and long-term health.